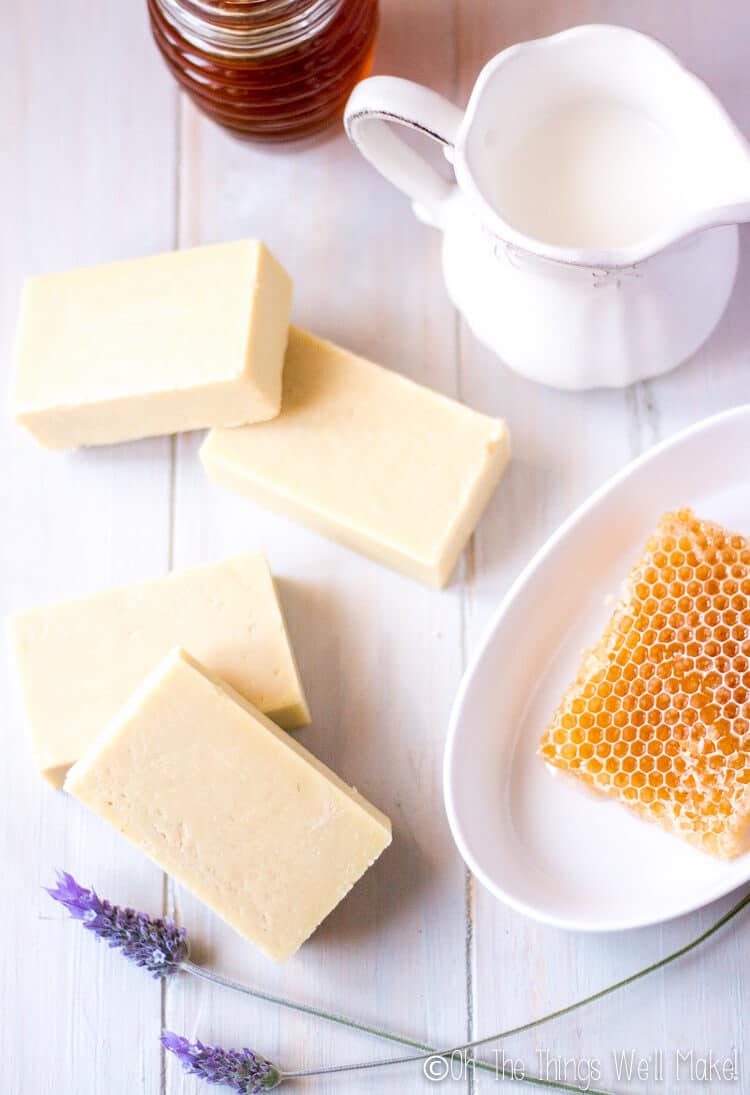

Gentle on the skin, and with a nice, creamy lather, this goat milk soap with honey is one of my favorites. Learn how to make soap with both milk and honey from scratch with this recipe.
Many of you have been asking for either a soap made with goat milk or one made with honey, so I decided to kill two birds with one stone and teach you how to make a soap with both goat milk and honey.
Because of the sugars in both milk and honey, they do provide a slight challenge when using in soap making, but I’ll share my tips and tricks to ensure you end up with pretty, light-colored bars of soap.
Watch how to make this goat milk soap with honey
Goat milk soap
Using milk in soap is a wonderful way to make a soap that is gentle on sensitive skin. It can help with eczema and psoriasis, and also has a nice, creamy lather.
I introduced working with goats milk in my pumpkin spice soap recipe, which as really just an adaptation of the easy, beginner soap. So many people asked for a goats milk soap, though, that I decided to formulate a new recipe which focused more on it and the techniques that can be used when working with it.
Adding milk to soap without burning it
While not difficult, working with milks in soap making can be slightly tricky. You need to take a few steps to ensure that the milk doesn’t burn when you mix it with the lye. Even when making a cold processed soap like this one, the heat from the reaction of the water and milk with the lye can cause the sugars in the milk to burn if you aren’t careful, resulting in a not-so-pretty, dark-colored bar that may even give off an unpleasant odor.
There are a couple of ways to prevent the milk from scalding. Most people freeze the milk before mixing it with the lye, and that method has always worked well for me. The heat generated when you mix the lye together with the liquids will melt the frozen milk rather than burn it. Those who don’t want to bother with pre-freezing can choose to add the milk at trace instead. (Trace is the point in soap making when the lye has emulsified with the oils and the soap is ready to be poured into molds.) At trace, there isn’t enough lye left to cause a heated reaction when the milk is added.
One of the benefits of freezing the milk is that you could potentially use a higher percentage of milk in your recipe. If you want to add the milk at trace, you’ll need to use enough water or other liquid, apart from the milk, to make the necessary lye solution for making the soap before adding in the milk.

Should you try to reach the gel phase with goat milk soap?
If you aren’t familiar with the gel phase, it’s basically a point in soap making when higher temperatures are reached and the soap begins to look gel-like. You can recognize a soap that has reached the gel phase because it normally gets a slightly translucent look to it which often makes the soap also look slightly darker. Some people aim to get their soaps to the gel phase, especially when working with colorants so that their soaps show off brighter, more vivid colors. Gelled soaps also tend to get slightly harder more quickly, probably because the soaps lose more water from evaporation at the higher temperatures.
To reach the gel phase, soaps are usually either heated right after being poured into the mold or at least well insulated to keep their heat in for the first day or two. It depends a lot on the recipe and the climate you are working in what needs to be done to reach a full gel phase.
With milk soaps, I don’t recommend trying to reach the gel phase. Milk soaps are prone to overheating which can lead to dark bars of soap that don’t smell very pleasant. It is also very easy to end up with a partially gelled soap that looks dark in the center and lighter and more opaque on the outside. While partially gelled soaps can still be used, they don’t look as nice as a uniform soap that is either gelled or not.
How to avoid reaching the gel phase
To avoid getting a partially gelled soap, you can either work the entire process cold as I have and then leave your soap molds uncovered in a cool place, or you can move the recently poured soaps into the fridge or freezer to finish the saponification process. I made the soap in the pictures when it was still cold in my house, and I had worked with frozen milk and cold oils. I didn’t put my mold into the freezer or fridge and you can see that my soaps turned out uniform in color.
If you are working in a warmer environment, I’d recommend placing your soap in either the fridge or freezer for the first 24 hours after having poured the soap into the molds to prevent getting a partially gelled soap.

Adding honey to soap
Honey is another nice additive for soap. The sugar in the honey helps make a nice, bubbly lather. While honey is nourishing for your skin, too much honey can result in a soft bar of soap (especially if you don’t account for the liquid in honey by reducing the amount of water in the recipe).
Just like when adding milk to soap, the sugars in honey could burn if things heat up too much. There are several ways to add the honey to the soap without that happening. One solution is to add the honey to the oils, rather than the water, before combining them with the lye solution. By doing it this way, you aren’t making the lye solution with the honey in it. I haven’t tried that method yet myself.
I, instead, add the honey as soon as the soap reaches a light trace, and haven’t had any problems.
Reaching trace when working with cold ingredients
One of the trickiest things about making soaps using cold ingredients is being able to recognize when you’ve reached “trace.”
Trace is the point in soap making when the oils and lye have emulsified and the saponification process begins. If you don’t reach trace, your soap won’t set correctly or may have pockets of oils and/or lye within the areas of the soap that have set.
Avoiding “false trace”
Normally, to ensure you have reached trace, I’d have you blend until the soap thickens up slightly, almost like pudding. The problem with working with cold temperatures, though, is that the thickness of the soap mixture can be misleading. At cold temperatures, it may take a very long time to thicken up. On the other hand, if you’ve melted your coconut oil, it may begin to slightly solidify again as everything cools, making it appear that the mixture is thickening. This can lead to people thinking the mixture has reached trace when it hasn’t. This recipe doesn’t use enough coconut oil that I think that you’ll have problems with false trace, but it is something I wanted you to be aware of.
If you find your recipe isn’t thickening up after blending for several minutes, and you plan on pouring it into the molds at a light trace (thinner mixture), you’ll want to take special care to ensure that everything is well blended and that there are no streaks of oil anywhere in the mixture. (If in doubt blend for longer than you think you need to!)
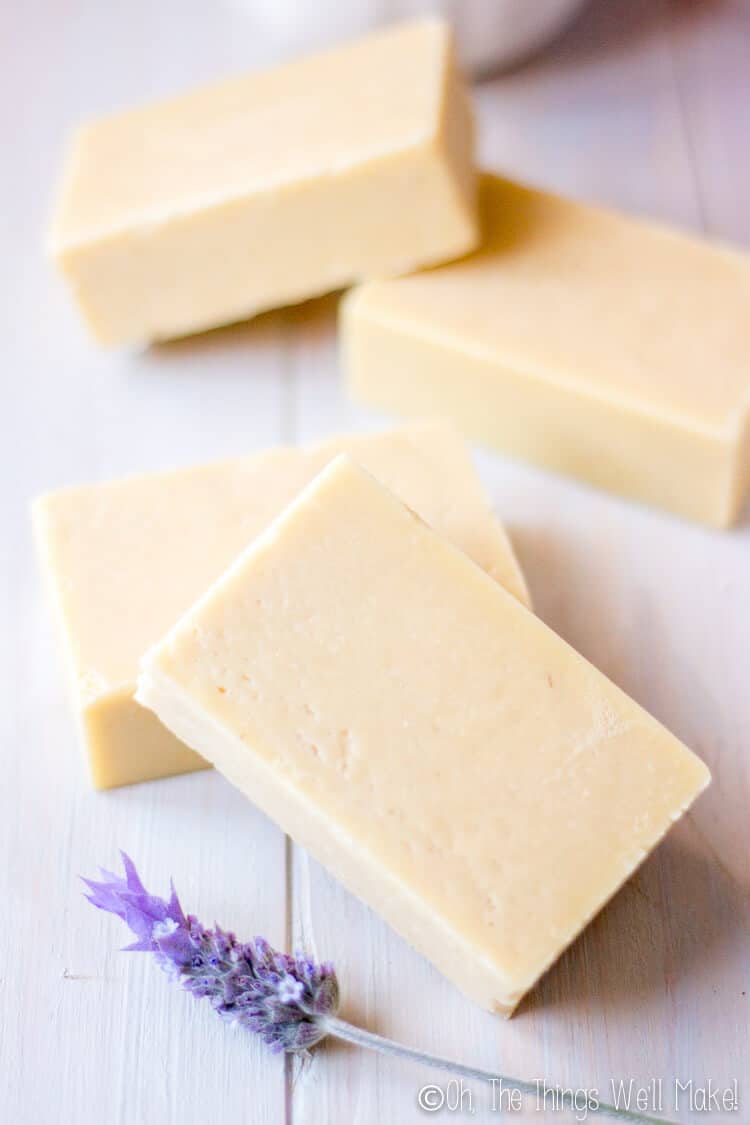

Goat milk soap with honey
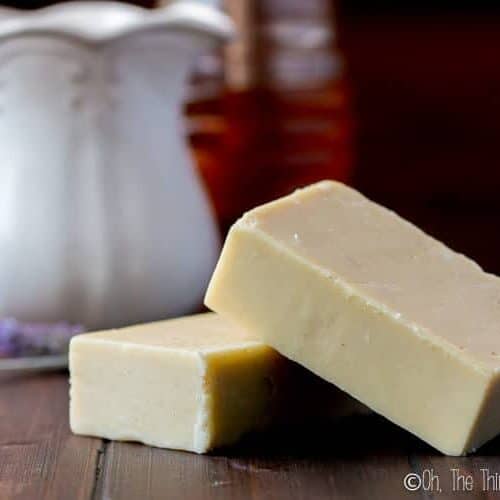

Goat Milk Soap with Honey
Fills up a loaf pan for 8-10 bars of soap
Materials
- 350 g olive oil
- 175 g coconut oil
- 75 g avocado oil
- 90 g distilled water
- 95 g goat milk
- 84.96 g lye
- 1 Tbsp. honey
Instructions
- Before beginning, freeze the goat milk to prevent it from burning when mixed into the lye solution. You can use it at the slushy stage or you can fully freeze it and use it in ice cube form.
- Weight out the distilled water and lye, and pour the lye into the container with water. (I like to use stainless steel bowls for this. Never pour the water into the container with lye.)
- Mix the lye into the water until it is fully incorporated. You’ll notice that the solution will heat up and become opaque, but if left will later cool off and become transparent again. (Work outside or in a well-ventilated area, and avoid inhaling the fumes. Protect your eyes and hands with gloves and goggles.)
- Add the frozen goat milk to the lye solution, and continue to stir as you incorporate it. It may turn slightly orange or brown due to the caramelization of the sugars in the milk reacting with the lye. To prevent it from burning, stir continuously until it has all melted and been fully incorporated into the solution.
- In a separate bowl, measure out the oils. You can weigh them all in the same bowl by taring (setting the weight to zero) your scale between oils. (In the video you’ll see that I was using solid coconut oil and didn’t melt it before using it. That was only to prove a point. I’d suggest melting the coconut oil to make the process move along more quickly and make things easier. There is no need to heat the other oils, though. If things get too hot you may end up scorching the sugars in the soap.)
- Add the lye solution to the oils and gently stir together until the lye solution has fully mixed with the oils.
- You can now begin to carefully blend together the oils and lye solution with an immersion blender. You’ll want to blend for several minutes, until your soap has reached “trace.” Trace is the point in soapmaking when the oils and lye have emulsified and the saponification process begins. (Read more about reaching trace in this soap above.)
- Once you’ve reached trace, you can add the honey and any essential oils or fragrance oils that you want to use. Blend until they’ve been fully incorporated.
- Pour the soap into soap molds. I used a silicone loaf pan for this recipe.
- If it is warm outside, you may want to pop your soap into the fridge or freezer to prevent having the soap partially gel. (You can read about the gel phase above.) Otherwise, leave it uncovered in a cool, ventilated area.
- After a couple of days, unmold the soap. If you’ve used a loaf type pan, cut the soap into bars.
- Allow the bars of soap to cure and dry for 4-8 weeks before using. (While you “can” use it before then without issues, the bars will harden and improve with time. Soaps will harden into longer-lasting bars and will mellow out during the curing process.)
- Enjoy your soap!
 Español
Español


 Easy Homemade Barbecue Sauce Recipe
Easy Homemade Barbecue Sauce Recipe
Amandine
Hello, could you recommend a switch for avocado oil ? Also could we use 100% goat milk for liquids instead of half and half with water ?
Thanks a lot !
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Yes, you can use all goat milk, but you will have to be very careful to freeze it so as not to scald the milk when mixing it with the lye.
Any changes in oils for the soap will have to be run through a lye calculator because different oils use different amounts of lye. Changes in oils can also greatly change the recipe.
I have posts that will give you more information about these switches…
how and why to use a lye calculator
The best oils for soap making
Ellen
Hello…. To use coffee grounds will the bars smell like coffee? I love coffee smell.
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Hi Ellen,
It’s very likely but will depend on the strength of the coffee remaining in the grounds. If you want more of a coffee scent, though, you can also brew up a strong coffee to use in place of the water. The grounds will also exfoliate the skin, so don’t overdo it with them!
Danuta
Hello Tracy, just a little not to say your recipes are well detailed and lovely to read (and make! the boba pearls and papadums is my fav). Thankyou for your time to record and teach your talents to others.
I’m going to try this recipe however I am looking for a goats milk shampoo rather than a soap. Is there a way this particular recipe can be altered at any step to make a shampoo instead of a soap?
Grateful for your help!
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Hi Danuta,
To be honest, I’m not a fan of soap based “shampoo bars” because the high pH of soap is very damaging to hair with time.
I make a shampoo bar (or liquid shampoo) for hair made with other surfactants. I’ve never tried incorporating goat milk powder, but you could experiment with it.
My main concern would be to keep it as dry as possible to keep it from growing bacteria or mold as milk can make things more prone to microbial growth.
Tammy
I use this recipe all the time! I’ve shared it with family and friends and they love the rich lather and wonderful aroma. Thank you for sharing with everyone
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Awesome! Thanks so much for letting me know! I’m so happy you enjoyed it! 🙂
Laetitia
Bonjour
Les 94 g de lessive correspondent à la soude (je possède de la soude en poudre…)? Merci
Tracy Ariza, DDS
I’m not sure what you’re referring to..
The 85g of lye?
It needs to be NaOH or sodium hydroxide. Baking soda will not work!
Shira
Can you add colloidal oatmeal to this recipe at all? If so, how much do you recommend for the above recipe?? Thanks in advance!
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Hi Shira,
Yes, that should be fine. I’m not sure about the amount. I’d probably start with around a half a Tablespoon and work up from there if you feel it needs more.
Leslie Denby
Just going to try this…just a note. If you live in cold place like England in a cold stone house …in the winter. Even leaving the soap overnight in the kitchen makes the soap brittle. Can you suggest how to cut brittle soap? Do you have to re melt it? Or can you put the young soap in a warm cupboard and warm it up? The ingredients are expensive especially with Aleppo soap I don’t want to throw another batch away.
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Yes, you can try that. I’ve had success at times warming a bar and then cutting with a warm knife. In the worst case scenario, yes, you can re-melt it. You’ll likely need to add more water to get it to melt, though- and it will probably have a more rustic look to it (be bumpier, etc.), so it’s best if you can do it the other way.
Debbie
Hi Karen,
I had a problem getting to trace yesterday, it took about 20 minutes before my stick blender got so hot that I decided to stop. It was a light/medium trace? I used 350g jojoba, 75g organic flax oil, 4g castor oil, and 175g coconut oil….(it should have been 171g). Are these oils not suitable do you think? I have made your original recipe a couple of times , omitting the water and adding more goats milk and it’s great, however I didn’t have any olive oil and wanted to test these. It is hardening, so maybe it’s OK? I would like your thought about why it took so long to get to trace though?
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Some oils aren’t very suitable for making soap. That seems like a lot of jojoba- and I haven’t really experimented with jojoba for soaps much because it’s quite expensive in comparison to other oils. You probably needed more of a solid oil- and olive is one of the few liquid oils that works well to make soaps being a large percentage of the recipe. (I have more about that in my post about the best oils for soap making.) I haven’t run your recipe through a lye calculator, but that’s another thing to keep in mind- different oils need different amounts of lye!
Debbie
Hi, I have made this soap twice and it’s really lovely. The first time I had to add more avocado oil as I ran out of the olive oil, but it was fine. I also managed to get to to a thick trace.
This time using the same recipe I used different oils instead of the olive oil…I used 75g organic unfiltered flax oil, 350g jojoba, 4g castor oil and 171g coconut oil. I sprinkled the lye pellets onto the frozen goats milk and stir until blended. All was fine, but I couldn’t get to the trace that I had before and after 20 minutes, (and my stick blender getting soo hot) I decided enough..it has thickened but I’d say it was a medium trace…..anyway I’ll see what turns out, but should it take this long/have I done something wrong? My family absolutely love this soap and going to the goat farm to get the milk is fun too!
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Hi Debbie,
The problem is that not all oils need the same amount of lye. Changing out an oil can drastically change a soap recipe. If you only change a small amount of one oil, it’s usually not enough to make a huge change, but changing out various oils or large quantities can make a HUGE difference.
I have posts about how to use a lye calculator and the best oils for soapmaking which better explain the problems you encountered.
Sarah V
Hi Tracy,
Just made this soap. Substituted Coconut Milk for the Goat’s Milk. Now to wait for it to cure enough to cut. I wish I could post a picture.
Tracy Ariza, DDS
Awesome!
You can always send photos to [email protected] if you like. 🙂